

The settings in this new GPO (for example, you set the minimum password length) will override the settings in the Default Domain Policy due to the higher precedence. What you can do is create a new GPO, link it to the domain level, and give it higher precedence than the Default Domain Policy. Password policy settings affect computers (see Figure 1) not user accounts! Linking and configuring a GPO to an OU will not configure the password policy differently for the users in that OU. Note: By using Group Policy, there can only be one password policy for the domain users. It is the responsibility of the DCs and databases located on them to filter each and every password that is attempted to be written to the database, to ensure the password meets the password policy settings.

The way the password policy works is that this GPO and the settings contained within this GPO configure the domain controllers (DCs) and the Active Directory databases located on them.
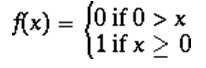
Figure 1 illustrates what those configurations look like and where you can find them in the Default Domain Policy.įigure 1. So why mention it here? Well, I still find admins and auditors not understanding how the domain password policy works, so let me explain it below.īy default in every installation of Active Directory, the Default Domain Policy establishes the domain password policy (for all users configured and stored in Active Directory, that is). The default behavior has not changed in those 14 years, so you can imagine how many people I have helped, not to mention how many times I have spoken about it. Over the past 14 years, I have been around the world helping admins, auditors, and security professionals understand how the domain password policy works in Active Directory.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
